Head and Neck Screening
Head and Neck
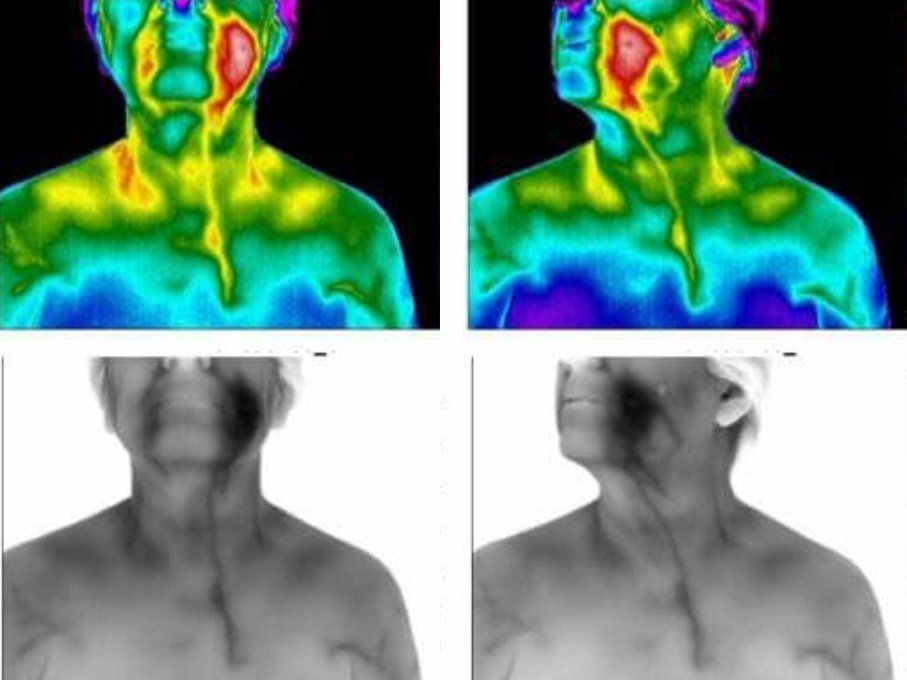
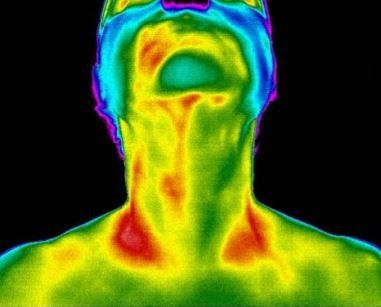
This thermal imaging series consists of 6 images and includes the head, neck and thyroid region. A cerebrovascular evaluation is also included in this screening.
Schedule An Appointment
Thermography can aid in the assessment of various dysfunctions, diseases, and other concerns in the head and neck region to include:
- Cerebrovascular Disease
- Oral Inflammation
- Thyroid Dysfunction
Cerebrovascular Disease
Cerebrovascular disease refers to a group of conditions that can lead to a cerebrovascular event, such as a stroke. These events affect the blood vessels and blood supply to the brain. If a blockage or hemorrhage prevents the brain cells from getting enough oxygen, brain damage can result.
Cerebrovascular diseases can develop in various ways, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and atherosclerosis, where plaque builds up in the arteries. Stroke, transient ischemic attack, aneurysm and vascular malformations are all types of cerebrovascular disease.
The earlier diagnosis of cerebrovascular disease such as the initial stage of a stroke is a worthy practical aspect of the clinical problem. One method of assessing blood flow in any portion of the body is by determining the temperature of that part and recognizing a variation from the physiologic state. Conditions which relate to flow of blood through the vessels of the head and neck are visible with thermography.
Oral Inflammation
Your oral health is more important than you might realize. The mouth is not an isolated ecosystem, but an integral part of the immune system, intimately connected to many other parts of the body. A bacterial imbalance in the mouth can create immune problems and inflammation in other parts of the body.
Bacteria is always present in the mouth. When it builds up on teeth it makes the gums prone to infection. The immune system then attacks the infection causing the gums to become inflamed. The inflammation will continue unless the infection is brought under control.
It is well established that periodontal disease, generally known as gum disease can be devastating to the mouth and is the leading cause of tooth loss and other oral problems. But did you know that gum disease can also have negative impact on other parts of the body? In fact, it is well documented that gum disease is linked with heart disease, stroke, diabetes and pregnancy complications. It may also increase the risk of various types of cancer including breast, pancreatic, esophageal and others.
Oral inflammation and infections will create higher temperatures on a thermogram, helping aid in a clinical diagnosis and treatment recommendations by your dentist.
Thyroid Dysfunction
The thyroid gland, simply known as the thyroid, is an endocrine gland that secretes thyroid hormones. It is a small butterfly-shaped gland found at the base of the neck. Through the hormones it produces, the thyroid influences almost all of the metabolic processes in the body.
Thermography offers a measurement of thyroid physiology. As such, it will not detect nodules or tumors but will provide a representation of physiologic dysfunction. When coupled with history, physical examination and other screening tools, thermography will provide a far greater picture of the thyroid function.
When performing head and neck thermography we look for significant temperature asymmetry between the lobes or a temperature variation between the thyroid gland and it's surrounding structures.