Early Detection Methods to Maintain Breast Health
CT Thermography • June 10, 2020
Early Detection Methods to Maintain Breast Health

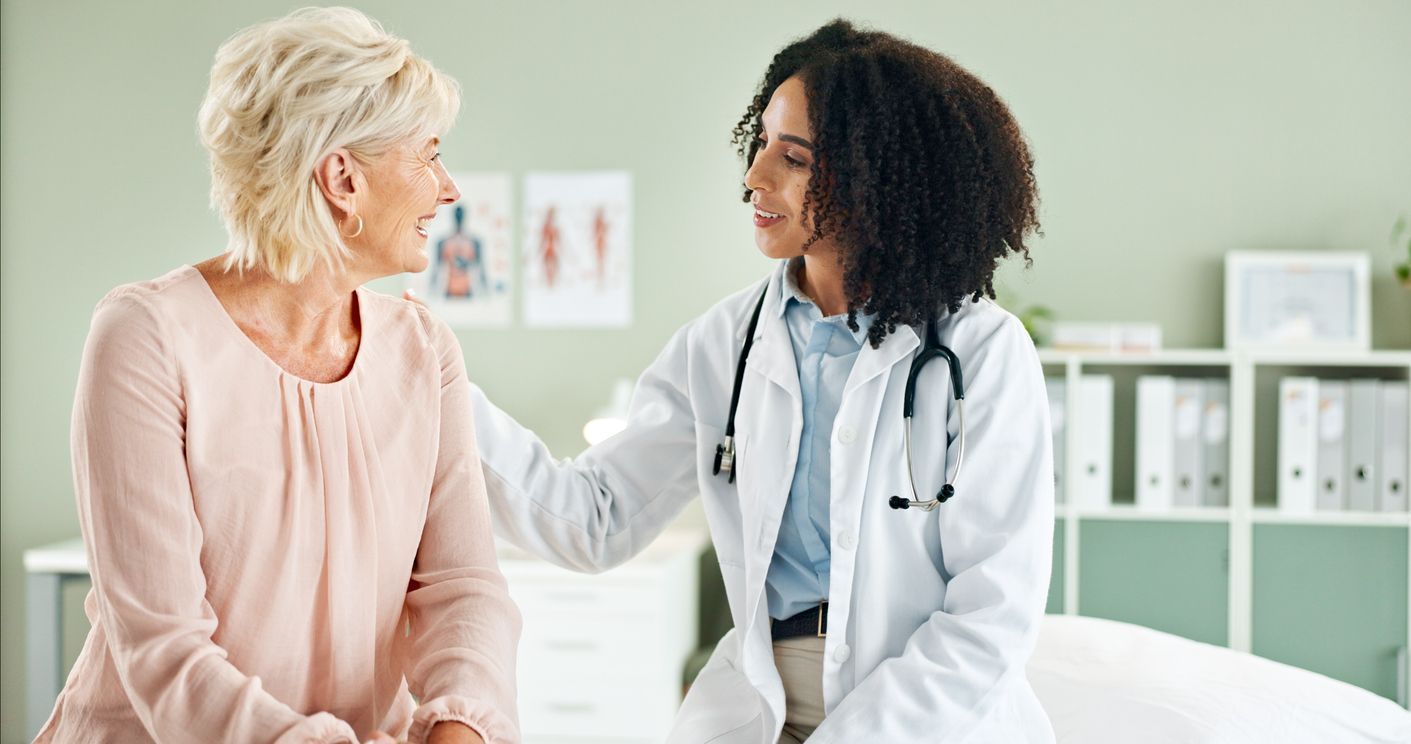
Breast cancer is the second most diagnosed cancer in women, affecting 1 out of every 8 women in the United States. Screening for breast cancer is important for all women, particularly women over 50. When breast cancer is detected early, the chances of survival is much higher- over 95% survival rate in the first five years. Here are a few tools and steps for maintaining breast health and detecting breast cancer early.
Lifestyle Factors
Factors that increase risk of developing breast cancer include:
- Alcohol use
- Being overweight
- Hormone therapy
- Birth control pills
Make sure you check in with your doctor to see if you may be able to minimize the lifestyle risks for breast cancer. A healthy lifestyle that includes maintaining exercise and a healthy diet, as well as limiting alcohol, can reduce the risk of developing cancer.
Regular breast self-exams
Women of all ages are encouraged to perform self-exams once a month. In the shower or in other comfortable positions, press the pads of your fingers gently along the entire breast and armpit. Look for lumps, tenderness, thickening of the skin, dimpling, or any other changes along this area. If you notice any changes, make sure that you contact your healthcare professional to schedule a screening. Keep in mind that not all hard lumps may be signs of breast cancer- they can also be signs of a benign condition, such as a cyst. If you are unsure about whether a lump should be checked, contact your provider for more information.
Screening tools
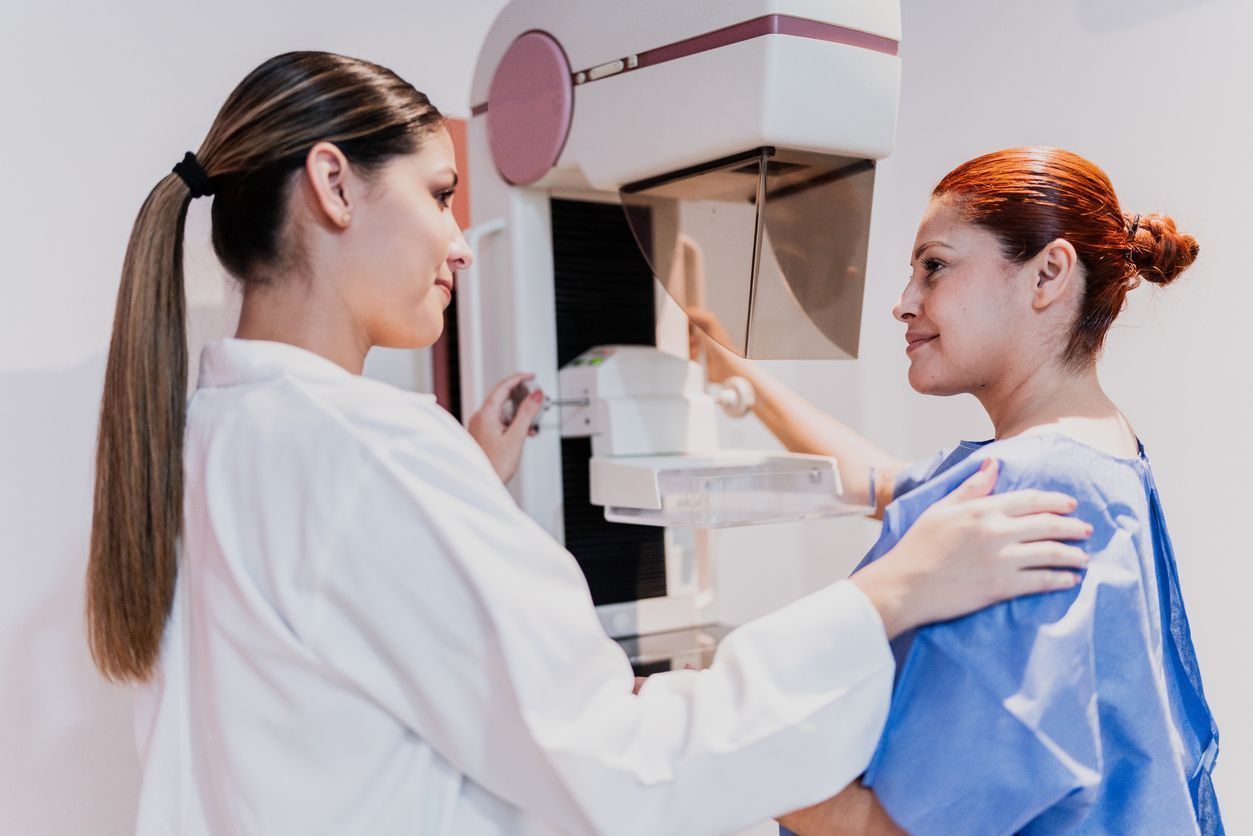
Women over 40 are advised to have an imaging of their breast every year. This will aid health professionals in detecting subtle abnormalities in your body. Combined with breast exams, they are another measure to double check that you are healthy.
Mammograms, or X-rays, may be used as an imaging tool. Although these are common, they focus on disease management and may include long term side effects. Thermography is a screening tool that is non-invasive and radiation free. It uses an infrared thermal camera to detect areas that need additional evaluation, such as abnormalities in breast tissue.
For more information about CT Thermography's services, check out our services
pag
e.